Large Animal Care
Equine
Dietary
Horses must have access to clean water and adequate food at all times. A general guide to feeding is to feed 1-2kg of food per 100kg of body weight, however this will be affected by the horse’s workload and the form of feed (hay, chaff or pasture). Water intake will vary depending on workloads and the weather, in summer a horse may drink 25-45 litres per day.
Feet
A horse’s feet will need to be trimmed by a farrier every 6-8 weeks, shoes may be required depending on workload (ridding on roads or rocky grounds). Should a horse’s feet not be trimmed regularly it can cause chipping, cracks, become uncomfortable for the horse, or result in health issues requiring veterinary treatments.
Worming
Having a clean paddock by removing your horse’s manure can help in worm control. The use of worming paste regularly will assist in treatment/prevention of worm infestations. It is recommended to use a worming paste every 6-8 weeks and rotate their worming paste to prevent resistance in worms. Faecal egg counts (FECs) can be performed in our local laboratory.
Vaccinations
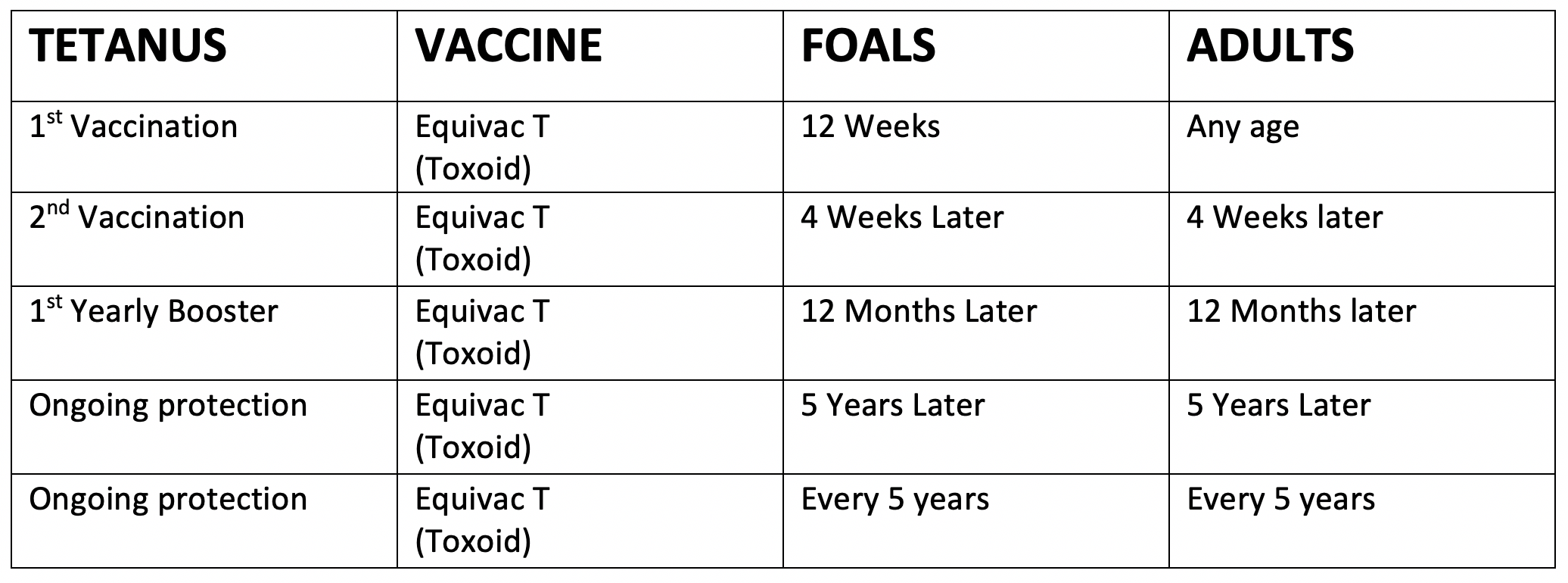
Tetanus in horses can be fatal. When infected your horse’s muscles can start to spasm, their body can become rigid or arching their back. This is due to the bacteria Clostridium tetani causing trouble in your horse’s nervous system. One of the main causes of Tetanus in horse’s is from a puncture wound (sometimes one that has not been noticed or seen) on an unvaccinated horse.
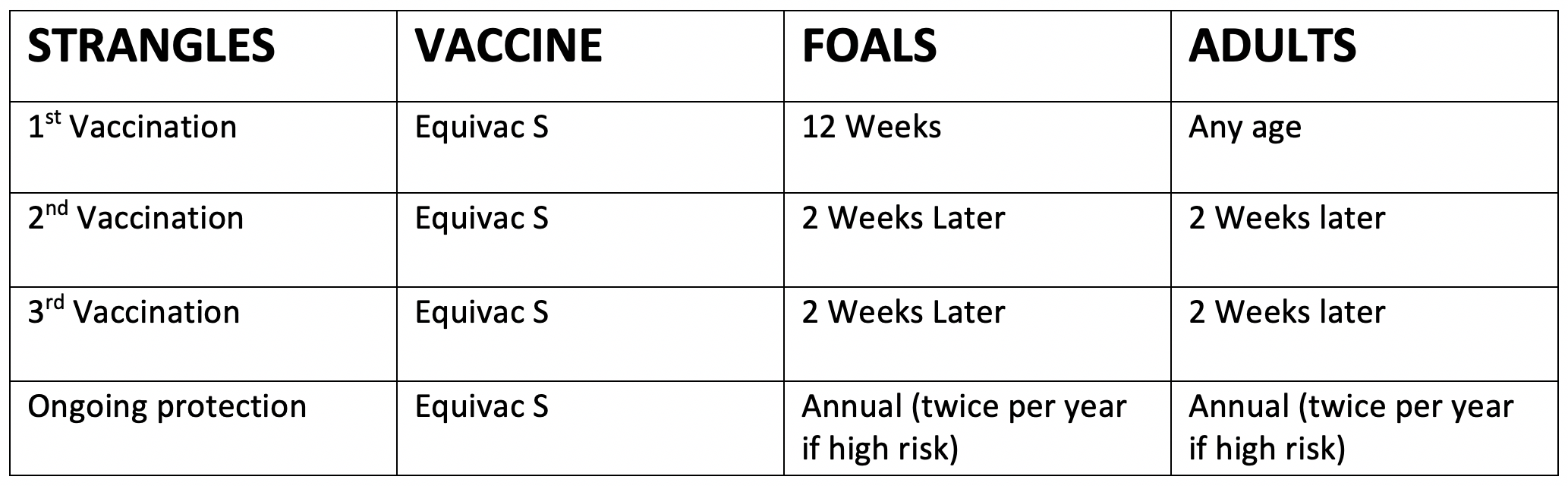
Strangles in horse’s is an upper respiratory infection caused by Gram-positive bacterium Streptococcus equi. It is often transmitted from horse to horse when they mix together (at events or new horse on property), it can also be transmitted from sharing water buckets from infected horses. Signs usually present as swollen lymph nodes resulting in abscesses causing difficulty swallowing, breathing, coughing fits, high fevers, lethargic and loss of appetite. Strangles can be fatal if suspected isolate the horse and contact a veterinarian.
Hendra vaccination is not a live or inactive virus, it contains soluble forms of G glycoprotein (sG0 of the Hendra Virus. All horses receiving the Hendra vaccination must be microchipped. The dose schedule is:
First dose Day 1
Second dose Day 21 – 42
Third Dose 6 months after the second dose
Annual booster 12 months after the third dose
Hendra virus is a serious and fatal. It can be transferred from horse to human for more information see the attached link: https://www.health.nsw.gov.au/Infectious/factsheets/Pages/hendra_virus.aspx
Vaccination guidelines for Strangles & Tetanus
Equivac TAT (antitoxin) should be used when any horse has attained an injury which breaks the skin.
Note: Tetanus takes 1-3 weeks to develop from date of original injury.
All vaccinations are given IM (intramuscular) except the Equivac TAT is given SC (under the skin)
Teeth
A horse’s teeth need to be checked every 12 months. If unchecked the teeth can become sharp or infected resulting in negative changes in temperament or health issues.